8.4 KiB
History of Boolean Algebra
- In 1849, George Boole published a scheme for describing logical thought and reasoning
- In the 1930s, Claude Shannon applied Boolean algebra to describe circuits built with switches
- Boolean algebra provides the theoretical foundation for digital design
Properties of Boolean Algebra
| Number | Col. A | Col. A Description | Col. B | Col. B Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 0 \cdot 0 = 0 |
1 + 1 = 1 |
||
| 2. | 1 \cdot 1 = 1 |
0 + 0 = 0 |
||
| 3. | 0 \cdot 1 = 1 \cdot 0 = 0 |
1 + 0 = 0 + 1 = 1 |
||
| 4. | if x = 0 then \overline{x} = 1 |
if x = 1 then \overline{x} = 0 |
||
| 5. | x \cdot 0 = 0 |
x + 1 = 1 |
||
| 6. | x \cdot 1 = x |
x + 0 = x |
||
| 7. | x \cdot x = x |
x + x = x |
||
| 8. | x \cdot \overline{x} = 0 |
$x + \overline{x} = 1 |
||
| 9. | \overline{\overline{x}} = x |
|||
| 10. Commutative | x \cdot y = y \cdot x |
x + y = y + x |
||
| 11. Associative | x \cdot (y \cdot z) = (x \cdot y) \cdot z |
x + (y + z) = (x + y) +z |
||
| 12. Distributive | x \cdot (y +z) = x \cdot y + x \cdot z |
x + y \cdot z = (x + y) \cdot (x + z |
||
| 13. Absorption | x + x \cdot y = x |
x \cdot (x + y) = x |
||
| 14. Combining | x \cdot y + x \cdot \overline{y} = x |
(x + y) \cdot (x + \overline{y}) = x |
||
| 15. DeMorgan's Theorem | \overline{x \cdot y} = \overline{x} + \overline{y} |
x + y = \overline{x} \cdot \overline{y} |
||
| 16. | x + \overline{x} \cdot y = x + y |
x \cdot (\overline{x} + y) = x \cdot y |
||
| 17. Consensus | x \cdot y + y \cdot z + \overline{x} \cdot z = x \cdot y + \overline{x} \cdot z |
(x + y) \cdot (y + z) \cdot (\overline{x} + z) = (x + y) \cdot (\overline{x} + z) |
Synthesis
In the context of binary logic, synthesis refers to the act of creating a boolean expression that evaluates to match a given truth table.
This is done by creating a product term for each entry in the table that has an output of 1, that also evaluates to 1, then ORing each product term together and then simplifying.
Example:
Given the below truth table, synthesize a boolean expression that corresponds.
x_1 |
x_2 |
f(x_1, x_2) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
f(0, 0)evaluates to true with the expression\overline{x}_1 \cdot \overline{x}_2f(0, 1)evaluates to true with the expression\overline{x}_1\cdot x_2f(1, 0)should provide an output of zero, so that can be ignoredf(1, 1)evaluates to true with the expressionx_1 \cdot x_2ORing all of the above expression together, we get:
f(x_1, x_2) = \overline{x}_1\overline{x}_2 + \overline{x}_1 x_2 + x_1x_2
\begin{multline}
= x_1x_2 \\
= x
\end{multline}
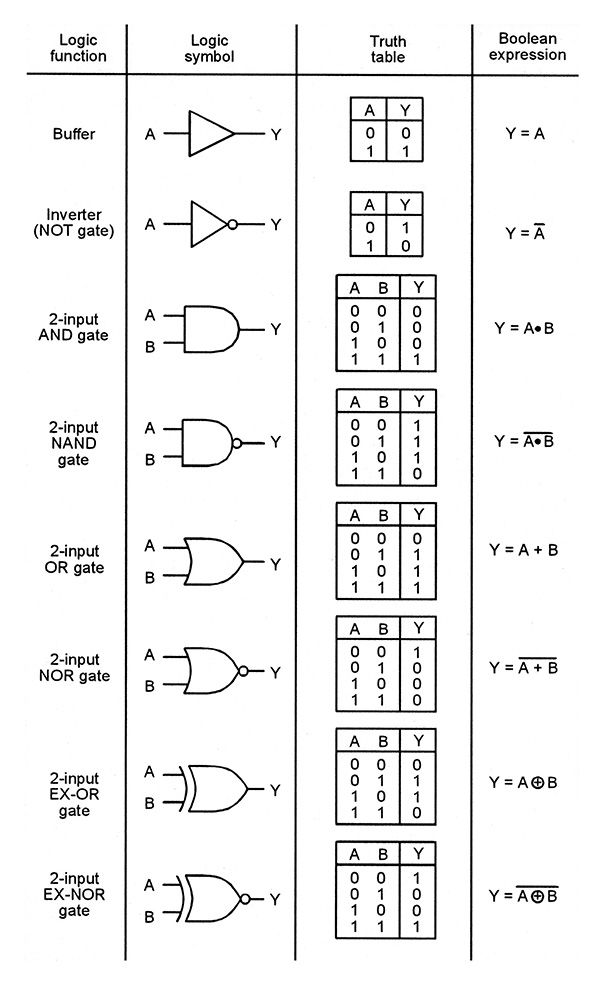
Logic Gates
NOT Gate
A binary NOT gate has a single input, and inverts that input (output is not the input).
Truth Table
x |
y |
|---|---|
| 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 |
Mathematical Expression
A NOT operation is mathematically expressed using a bar:
y = \bar{x}
AND Gate
An AND gate will only output a 1 if both inputs are a one (input one and input two are enabled).
Truth Table
x_1 |
x_2 |
y |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
Mathematical Expression
An AND operation is mathematically expressed using a times symbol, or with no symbol at all:
y = x_1 \cdot x_2 = x_1x_2
NAND Gate
A NAND gate outputs a 1 unless both inputs are enabled (input one and input two are not enabled).
Truth Table
x_1 |
x_2 |
y |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
Mathematical Expression
A NAND operation is mathematically expressed using a bar over an AND operation:
y = \overline{x_1 \cdot x_2}
OR Gate
An OR gate outputs a 1 if either or both inputs are enabled (if input one or input two is enabled).
Truth Table
x_1 |
x_2 |
y |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
Mathematical Expression
A mathematical OR is notated with a + symbol.
y = x_1 + x_2
NOR Gate
A NOR gate outputs a one if neither gate is enabled.
Truth Table
x_1 |
x_2 |
y_1 |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
Mathematical Expression
A NOR operation is expressed using a bar over an OR operation.
y = \overline{x_1 + x_2}
XOR Gate
An XOR gate is on if one input is enabled, but not both (exclusively one or the other).
Truth Table
x_1 |
x_2 |
y |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
Mathematical Expression
An XOR operation is expressed using a circle around an addition symbol:
y = x_1 \oplus x_2
XNOR Gate
An XNOR gate is on if neither input is enabled, or both inputs are enabled.
Truth Table
x_1 |
x_2 |
y |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
Mathematical Expression
An XNOR operation is expressed using a bar over an XOR operation:
y = \overline{x_1 \oplus x_2}